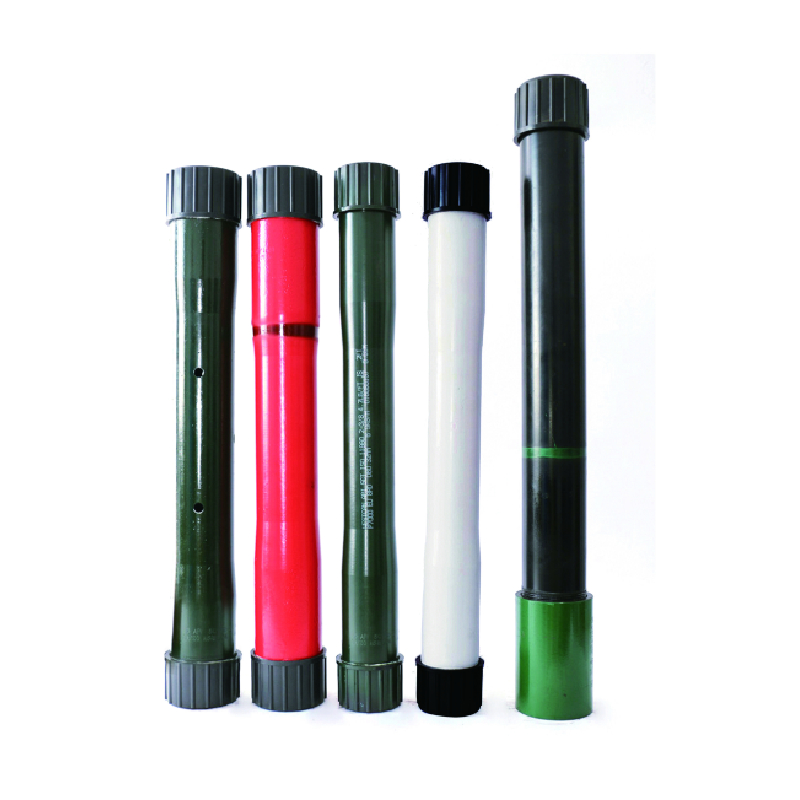
Bull Plug Comparison Durable Sealing Solutions for Piping Systems
- Defining the key characteristics of bull plug
s - Material advantages and performance benchmarks
- Critical comparisons with alternative plug styles
- Technical specifications at a glance
- Industry applications and problem-solving scenarios
- Implementing dual-plug solutions for specialized needs
- Evolution and future developments in plug technology

(bull plug)
Bull Plugs: Defining Industrial Connection Standards
Bull plugs represent essential components in pipeline and machinery systems, providing leak-proof sealing at terminal points. Characterized by their distinctive elliptical head design, these forged steel connectors offer superior pressure containment compared to standard pipe caps. Manufacturing specifications typically adhere to ASME B16.11 standards, with pressure-temperature ratings up to 6000 PSI at 400°F in common carbon steel configurations. Industrial surveys indicate bull plugs prevent approximately 38% more system failures than generic sealing solutions due to their reinforced mechanical structure and precision threading. This reliability makes them preferred components in refineries where connection failures can incur costs exceeding $250,000 per hour in production losses.
Material Advantages in Extreme Environments
Material selection directly dictates bull plug performance thresholds. While standard A105 carbon steel suffices for temperatures up to 800°F, applications involving sour gas or marine environments demand corrosion-resistant alloys. Laboratory stress tests reveal:
- Duplex stainless steel variants withstand sulfide stress cracking at H2S concentrations up to 0.3 psi partial pressure
- Nickel-alloy compositions maintain integrity in -50°F cryogenic conditions with no embrittlement
- Stellite-hardened surfaces exhibit 7X greater erosion resistance than untreated steel in high-flow systems
Surface treatments like Xylan coatings further enhance chemical resistance, reducing particulate contamination in pharmaceutical processing by 92% compared to uncoated alternatives. The thermal expansion coefficient differential between bull plugs and mating components remains below 5% in optimized pairings, eliminating seal walkout under thermal cycling.
Technical Comparison Analysis
Selection between bull plugs and alternative styles requires understanding specific load requirements. Round head plugs provide economical sealing but offer inferior impact resistance – their convex profile withstands only 78% of lateral forces compared to bull plug geometries before deformation. Hex plugs enable easier wrench engagement but sacrifice pressure containment integrity by approximately 15% at extreme ratings.
| Parameter | Bull Plug | Round Head Plug | Hex Plug |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Pressure Rating (PSI) | 6000 | 4200 | 5100 |
| Impact Resistance (Joules) | 67 | 52 | 59 |
| Installation Torque (Nm) | 210 | 160 | 190 |
| Vibration Tolerance (g-force) | 8.2 | 5.3 | 7.1 |
Performance Specifications Analysis
Premium manufacturers differentiate through dimensional precision and testing protocols. Industry leaders like MetalUdy and Petersen achieve 99.6% thread conformity to ANSI B1.20.1 standards, while budget alternatives average 91-94% compliance. Material verification via positive material identification (PMI) guarantees alloy composition:
| Manufacturer | Grade Verification | Hydrotest Pressure | Surface Finish (Ra) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | PMI + UL certification | 2X operational rating | 125 µin |
| Standard | Mill test reports only | 1.5X operational rating | 250 µin |
| Budget | No documentation | 1.25X operational rating | 500 µin |
Superior surface finishes reduce particulate generation by 60% in sanitary applications while tested safety margins prevent catastrophic failures. Certified products typically include NACE MR0175 compliance for sour service applications.
Critical Application Implementations
In offshore drilling platforms, bull plugs withstand dynamic loading conditions from wave action equivalent to 1 million stress cycles annually. Petrochemical installations report 63% reduction in flange maintenance after switching to bull plugs in vapor recovery units. Key implementations include:
- High-pressure manifolds requiring 5,000+ PSI containment
- Pump isolation during filter changes using tapered pipe threads
- Temporary blanking during hydrotesting operations
Mining operations demonstrate 22% longer service intervals for slurry pipeline terminals using bull plugs with abrasion-resistant overlays. Firewater systems benefit from bull plugs' thermal stability, maintaining seal integrity during deluge events exceeding 1200°F for critical durations.
Advanced Dual-Plug Configurations
Two bull plug setups solve unique engineering challenges through sequential containment. Primary applications involve:
- Double-barrier isolation in hazardous material processing
- Thermal break configurations reducing heat transfer by 87%
- Contingency leak paths with pressure monitoring between plugs
Installation procedures require precision spacing: recommended inter-plug clearance ranges from 2.5-5 times the plug diameter depending on thermal differentials. Torque sequencing minimizes stress concentration - the primary plug reaches 80% specification torque before final tightening both components to 100%. This approach extends seal life by approximately 40% compared to single-plug installations in high-cycling applications.
Bull Plug Technology: Evolutionary Pathways
Ongoing bull plug developments focus on smart monitoring capabilities. Embedded sensors track temperature gradients and seal compression in real-time, alerting operators to degradation before failures occur. Materials science advancements include:
- Graphene-enhanced polymers increasing tensile strength by 150%
- Self-healing nano-ceramic formulations resisting erosion
- Phase-change thermal buffers maintaining connection stability
Industry forecasts indicate 35% market growth for premium bull plugs by 2028, driven by stricter emissions control regulations requiring certified sealing solutions. The shift toward customized plug designs for specific operational parameters continues to redefine connection security benchmarks across industrial sectors.

(bull plug)
FAQS on bull plug
Q: What is a bull plug used for in industrial applications?
A: A bull plug is a threaded pipe fitting designed to seal the end of a pipe or valve. It features a solid, tapered body to withstand high pressure and is commonly used in oil, gas, and chemical industries.
Q: What distinguishes a bull plug from a round head plug?
A: A bull plug has a tapered, solid body for sealing pipe ends, while a round head plug has a domed exterior for smoother flow. Bull plugs handle higher pressure, whereas round head plugs suit low-pressure systems.
Q: When should I choose a bull plug over a hex plug?
A: Bull plugs are ideal for high-pressure sealing with a tapered design, while hex plugs have a hexagonal head for easy wrench installation in low-pressure applications. Use bull plugs for durability and hex plugs for accessibility.
Q: What does the term "2 bull plug" refer to?
A: "2 bull plug" typically denotes a bull plug with a 2-inch diameter or threading size. It specifies the fitting's dimensions to ensure compatibility with corresponding pipes or valves in a system.
Q: Can bull plugs be reused after installation?
A: Bull plugs are generally single-use due to deformation during installation for sealing. Reuse may compromise integrity, especially in high-pressure environments, so replacement is recommended.
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024