2 月 . 19, 2025 03:32
Back to list
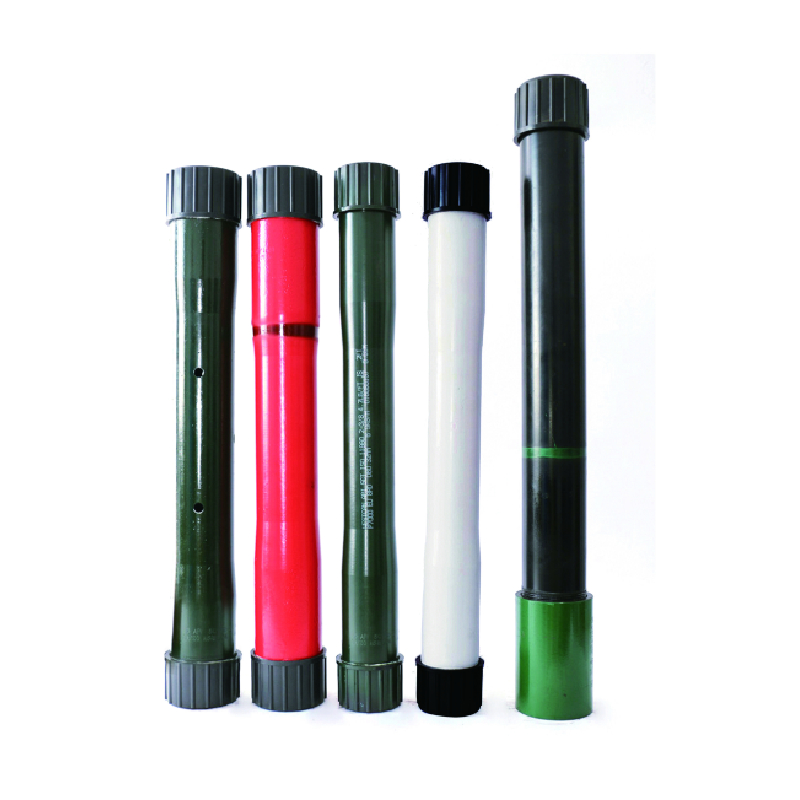
bull plug wellhead
Bull plugs in wellhead systems play an integral role in the petroleum industry, contributing significantly to the overall safety and efficiency of drilling operations. On the surface, they might appear as simple components, but their function is far from trivial. Understanding these components from an experienced perspective, rooted in technical knowledge, offers insight into why they are indispensable.
In terms of installation and utilization, trust in the quality and performance of bull plugs cannot be overstated. It is crucial to source these components from reputable manufacturers who adhere to stringent industry standards such as API Specification 6A. This standard ensures that all components can withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, certifying their reliability in safeguarding wellhead integrity. Users must ensure these products are traceable and come with comprehensive inspection reports, fostering trust and peace of mind in their use. Real-world experience with bull plugs demonstrates their practical value. In many documented cases, bull plugs have averted potential disasters by sealing off sections of a wellhead during emergencies, preventing uncontrolled flow of oil or gas. This functionality proves essential when unexpected downhole conditions arise, allowing for immediate containment until further action can be taken. Such instances highlight the critical, often lifesaving role these components play and why operational teams place significant trust in their effectiveness. Furthermore, routine maintenance of wellhead systems often involves the removal and inspection of bull plugs for wear and tear. Experienced operators emphasize that regular checks can prevent premature failures. Inspections can detect issues like thread damage or corrosion early, which, if left unattended, could lead to substantial operational interruptions or hazards. Thus, a proactive maintenance strategy is advised, combining technical inspections with adherence to industry-best practices, to maintain well integrity over the lifespan of the operation. Overall, the application of bull plugs extends well beyond their initial perception. Their integration within wellhead systems is a testament to the necessary blend of experience, expertise, and trustworthiness required in oilfield operations. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, the foundational role of bull plugs remains unchanged, driven by a legacy of engineering excellence and safety priorities. For those engaged in the oil and gas sector, understanding the nuances of these critical components is not merely an academic exercise but a professional imperative that reinforces the industry's commitment to safe and efficient energy production.


In terms of installation and utilization, trust in the quality and performance of bull plugs cannot be overstated. It is crucial to source these components from reputable manufacturers who adhere to stringent industry standards such as API Specification 6A. This standard ensures that all components can withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, certifying their reliability in safeguarding wellhead integrity. Users must ensure these products are traceable and come with comprehensive inspection reports, fostering trust and peace of mind in their use. Real-world experience with bull plugs demonstrates their practical value. In many documented cases, bull plugs have averted potential disasters by sealing off sections of a wellhead during emergencies, preventing uncontrolled flow of oil or gas. This functionality proves essential when unexpected downhole conditions arise, allowing for immediate containment until further action can be taken. Such instances highlight the critical, often lifesaving role these components play and why operational teams place significant trust in their effectiveness. Furthermore, routine maintenance of wellhead systems often involves the removal and inspection of bull plugs for wear and tear. Experienced operators emphasize that regular checks can prevent premature failures. Inspections can detect issues like thread damage or corrosion early, which, if left unattended, could lead to substantial operational interruptions or hazards. Thus, a proactive maintenance strategy is advised, combining technical inspections with adherence to industry-best practices, to maintain well integrity over the lifespan of the operation. Overall, the application of bull plugs extends well beyond their initial perception. Their integration within wellhead systems is a testament to the necessary blend of experience, expertise, and trustworthiness required in oilfield operations. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, the foundational role of bull plugs remains unchanged, driven by a legacy of engineering excellence and safety priorities. For those engaged in the oil and gas sector, understanding the nuances of these critical components is not merely an academic exercise but a professional imperative that reinforces the industry's commitment to safe and efficient energy production.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024
Related Products