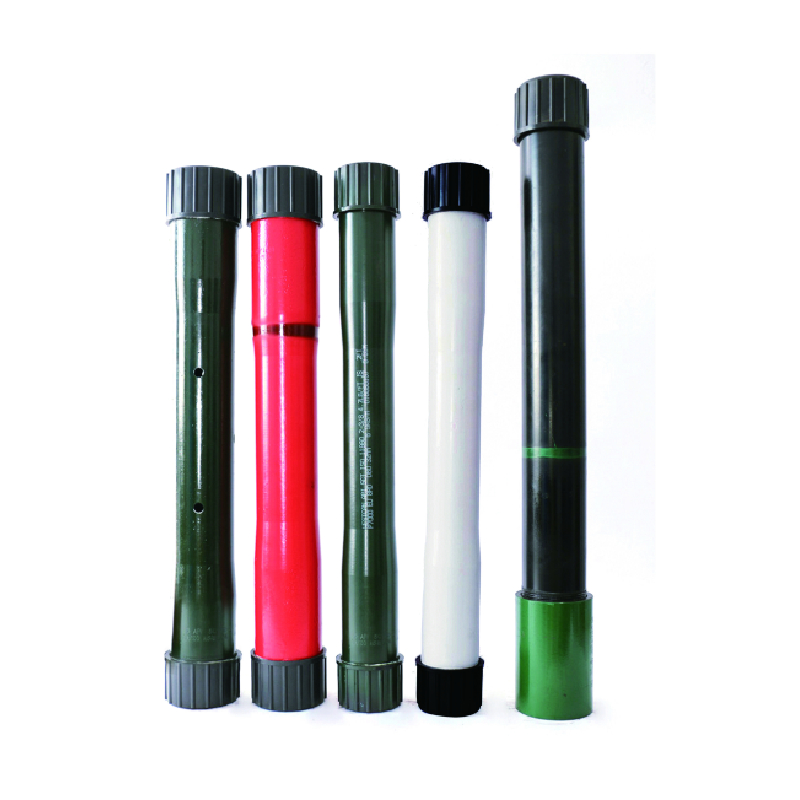
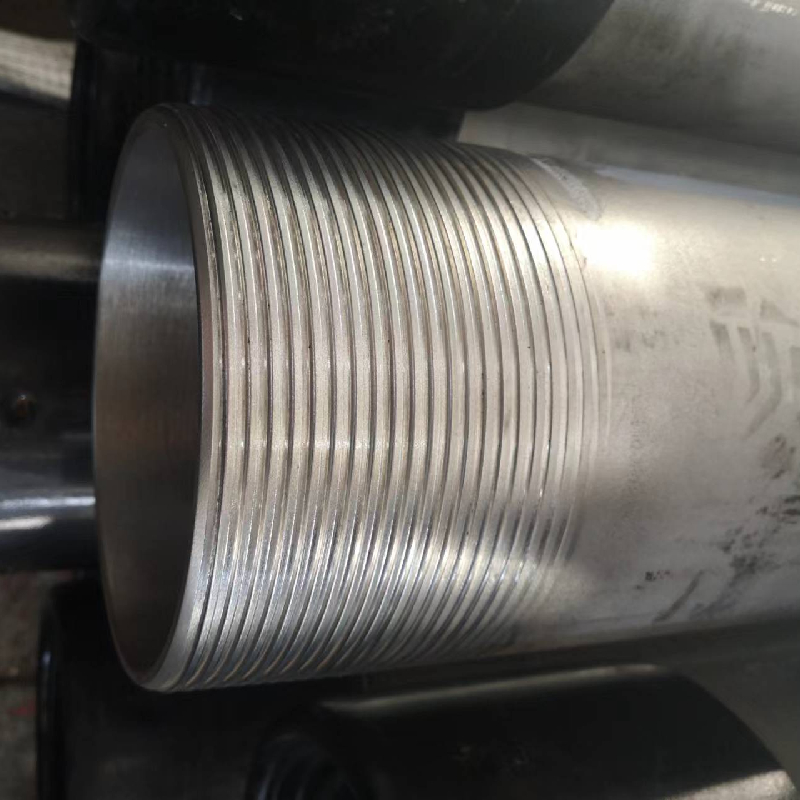
coupling for tubing
Coupling for Tubing An Essential Component in Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, the extraction of resources relies heavily on a mechanical system known as tubing. Tubing is a critical part of the drilling process through which hydrocarbons flow from the reservoir to the surface. Among the many components involved in the tubing system, couplings play a vital role in ensuring the strength, integrity, and reliability of this system. This article delves into the purpose, types, and significance of couplings in tubing applications.
Understanding Couplings
A coupling is a device used to connect two segments of tubing or pipe. Its primary role is to join lengths of tubing, ensuring a tight seal that can withstand pressure and environmental conditions. Couplings must be robust enough to handle the stresses and strains that occur in a typical oil and gas extraction process. Given the harsh conditions often faced in this industry, including high pressures and corrosive substances, the choice of coupling material and design is critical.
Types of Couplings
Couplings can be categorized based on their design and functionality
. Here are some common types1. Threaded Couplings These are the most traditional coupling types. They consist of male and female threads that screw together to create a tight seal. Threaded couplings are widely used due to their simple installation process and cost-effectiveness. However, they may be susceptible to wear and tear over time.
2. Butt Welded Couplings In this type, the ends of the tubing are aligned and welded together. This creates a continuous piece of tubing, eliminating potential weak points found in threaded systems. Butt welding is often preferred for high-pressure applications due to its durability.
3. Socket Welded Couplings Socket weld couplings involve inserting one piece of tubing into a socket on another piece before welding them together. This method offers a tighter seal and greater strength than threaded couplings, making them suitable for high-pressure systems.
coupling for tubing

4. Flanged Couplings Flanged couplings involve flanges that are bolted together. This type of coupling is highly versatile and allows for easy disconnection for maintenance or inspection. Flanged connections are typically found in larger diameter piping systems.
5. Compression Couplings These couplings are used to connect two tubings without the need for welding or threading. They rely on a compression mechanism to create a seal. This type is often used in situations where quick assembly or disassembly is necessary.
Materials Used in Couplings
The materials used in the manufacturing of couplings play a crucial role in their performance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialty alloys that can resist corrosion and high temperatures. The choice of material depends on the operating environment and specific conditions of the drilling site. For example, stainless steel is often chosen for its resistance to corrosion, while carbon steel may be preferred for its strength-to-weight ratio.
Importance of Proper Alignment and Installation
For couplings to perform effectively, proper alignment and installation are paramount. Misalignment can lead to stress concentrations that may cause failure over time. Techniques such as laser alignment help in ensuring that the tubing sections are aligned correctly before coupling them together. Ensuring a proper seal during installation can prevent leaks, which is crucial both for safety and for maintaining the efficiency of the extraction process.
Conclusion
In summary, couplings are indispensable components in tubing systems within the oil and gas industry. They provide the necessary connections between tubing segments, allowing for the safe transportation of hydrocarbons from deep underground to the surface. The variety of coupling types available ensures that various needs and specific environmental conditions can be met adequately. Proper material selection and installation techniques are critical in maximizing the longevity and integrity of these couplings. As technology advances, new materials and techniques will continue to emerge, further enhancing the effectiveness of couplings in tubing systems, and ultimately supporting a more efficient and safer oil and gas extraction process.
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024