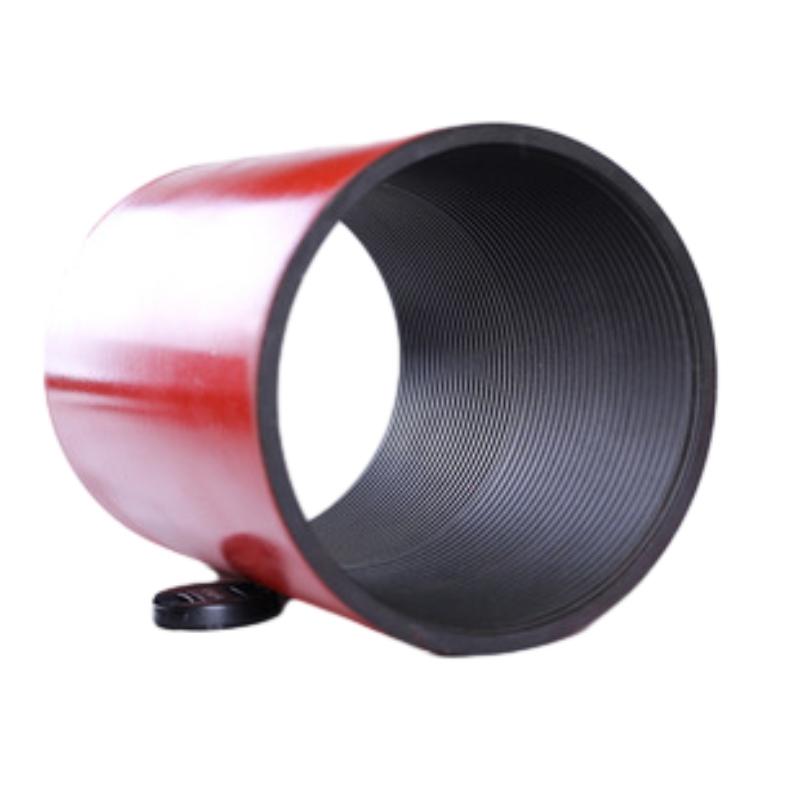
Exploring the Benefits and Applications of 1% 202 NPT Stainless Steel Couplings in Plumbing Systems
Understanding 1% 202 NPT Stainless Steel Couplings
Stainless steel couplings are essential components in various industries, used primarily for connecting pipes in fluid and gas transfer applications. One common variation, the 1% 202 NPT stainless steel coupling, exemplifies the versatility and reliability of stainless steel fittings in piping systems. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, applications, and advantages of this specific coupling type.
Characteristics of 1% 202 NPT Stainless Steel Couplings
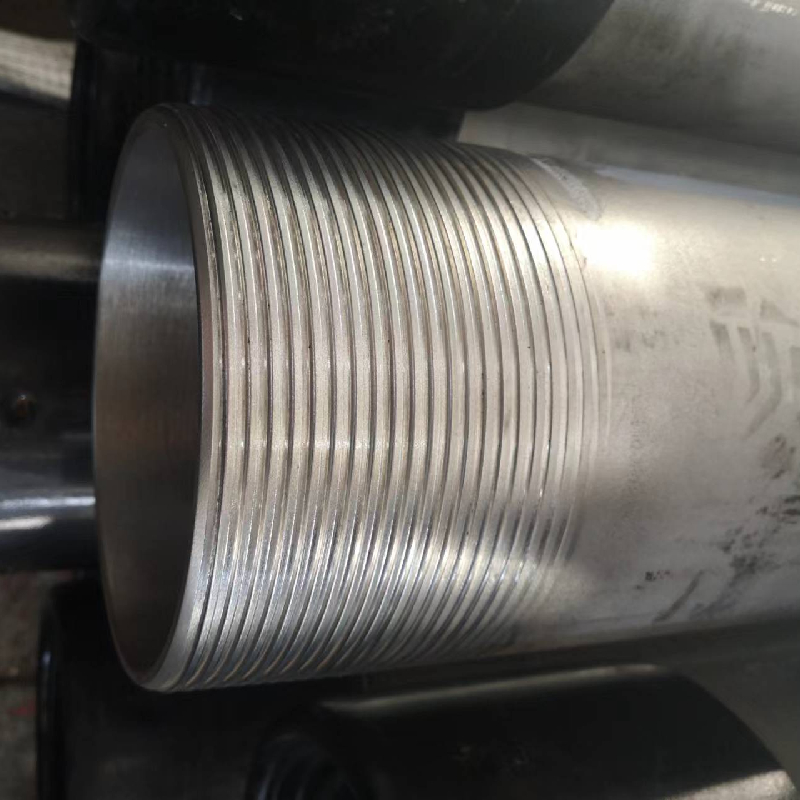
The designation 202 refers to a specific grade of stainless steel, which is an alloy that contains chromium, nickel, and manganese. Typically, 202 stainless steel features a lower nickel content than other grades, such as 304, which imparts unique properties. The NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered, indicating that these couplings have threads that allow for a tight seal when connecting pipes.
These couplings are designed to withstand various environmental conditions. The 1% specification indicates that there may be a particular add-on element or feature that distinguishes these couplings in specific applications. However, the standout attributes remain their corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and the ability to maintain structural integrity even in extreme temperatures.
Applications of 1% 202 NPT Stainless Steel Couplings
1% 202 NPT stainless steel couplings find a wide range of applications across multiple industries. They are commonly used in
1. Plumbing Systems These couplings are vital in residential and commercial plumbing, enabling secure connections between pipes for water supply and drainage systems. Their corrosion resistance makes them ideal for use in wet environments.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for transporting chemical substances, where maintaining the integrity of piping systems is crucial. The NPT design ensures leak-proof connections, preventing unwanted spills or reactions.
3. Food and Beverage Industry Sanitation is critical in this sector, and stainless steel couplings' non-reactive nature supports hygiene standards. They are often used in beverage manufacturing and food processing facilities where clean, safe transport of liquids is essential.
1 2 npt stainless steel coupling

4. Oil and Gas Industry These couplings are employed in pipelines that transport crude oil, natural gas, and other fluids, where they demonstrate resilience against corrosive substances and high-pressure conditions.
5. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, the couplings are utilized to connect ductwork and piping, ensuring efficient airflow and temperature control.
Advantages of Using 1% 202 NPT Stainless Steel Couplings
1% 202 NPT stainless steel couplings offer several benefits, making them a preferred choice for many engineering applications
- Corrosion Resistance One of the primary advantages of stainless steel is its ability to resist rust and other forms of corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan for the piping system.
- High Strength and Durability Stainless steel couplings can withstand significant pressure and stress, making them suitable for high-demand applications.
- Temperature Resistance These couplings perform well under varying temperature conditions, from cryogenic to elevated temperatures, allowing for flexible use in diverse environments.
- Easy Installation The tapered threading of NPT fittings ensures a tight seal, simplifying installation without the need for additional sealing materials.
- Low Maintenance Owing to their robust nature, stainless steel couplings require less maintenance compared to other materials, thereby reducing long-term operational costs.
In conclusion, 1% 202 NPT stainless steel couplings represent an effective solution for safely connecting pipes in numerous applications. Their unique combination of strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion renders them indispensable in various industries. Understanding their properties and uses can help engineers and maintenance professionals make informed decisions when designing or maintaining piping systems.
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024