1 月 . 15, 2025 09:38
Back to list
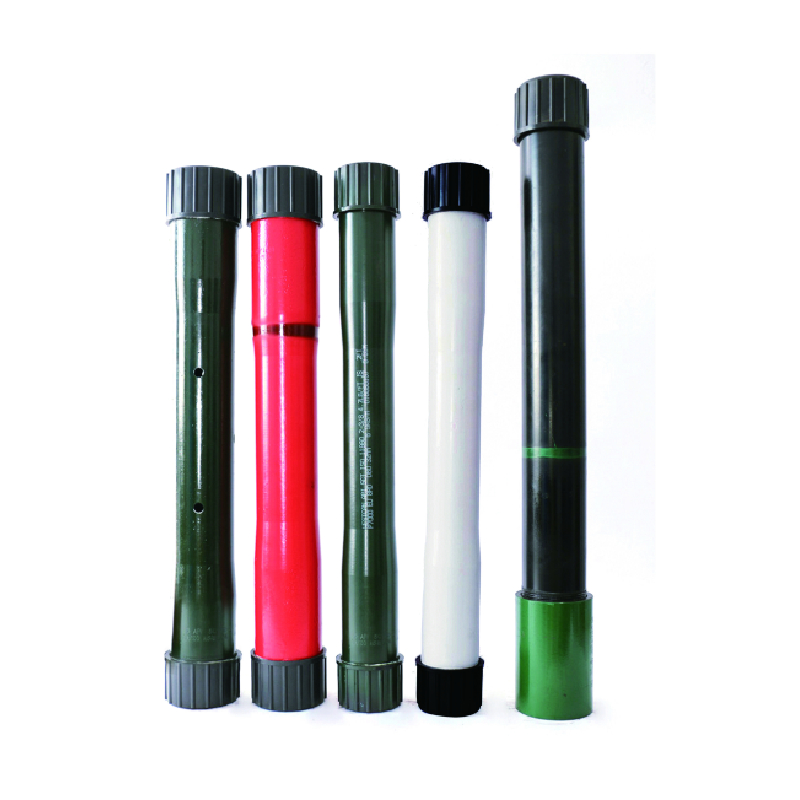
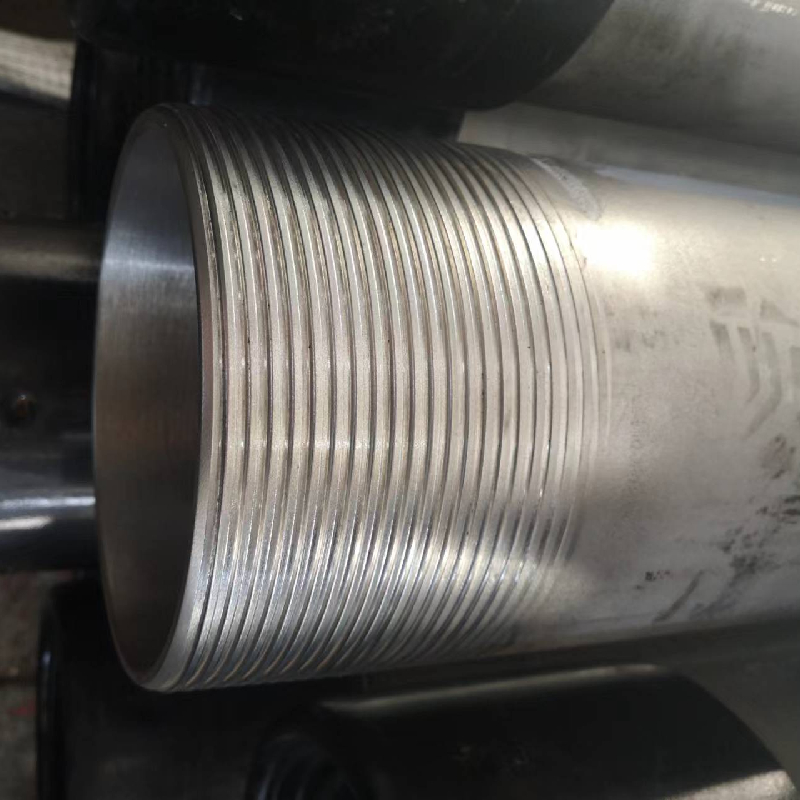
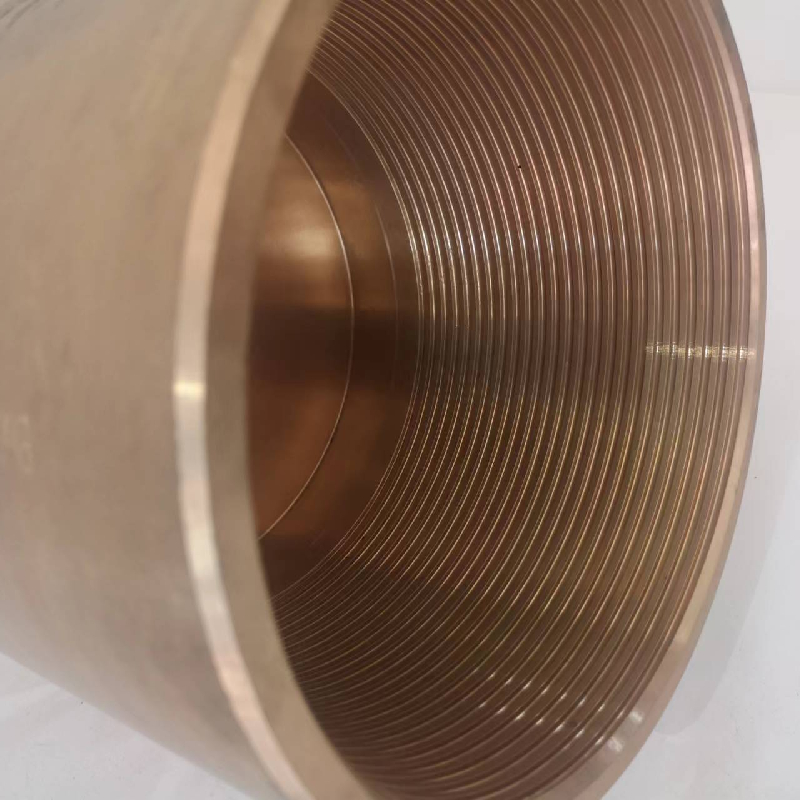
Tubing Coupling
Navigating the complexities of the pipe mill industry involves a thorough understanding of various production processes, material selection, quality control, and technological advancements. As a critical segment in the manufacturing domain, pipe mills produce a wide range of tubular structures primarily used in sectors like oil and gas, construction, and water supply. This article delves into the intricate world of pipe mills, offering insights drawn from actual experience, deep expertise, and corroborated by authoritative sources.
The expertise required in a pipe mill extends beyond mere operation. It involves understanding market demands, which drive production rates and product diversity. Experience shows that keeping abreast of technological innovations is crucial. For instance, the adoption of 3D modeling and automation in pipe design has radically improved precision and efficiency, reducing material waste and production time. Trust in the pipe mill's capabilities is built over time through consistent product quality and compliance with international standards such as ASTM, API, or ISO. These certifications not only validate the manufacturing process but also assure clients of the product's reliability and performance. Established mills often conduct third-party audits and client visits to further enhance transparency and trustworthiness. Indeed, the evolution of pipe manufacturing technology continues to create new opportunities and challenges. Modern mills are integrating smart technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) to monitor equipment health in real-time, predict downtimes, and optimize production schedules. Such advancements not only enhance the production process but also contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient operation. The pipe mill industry, with its blend of traditional practices and cutting-edge innovations, stands as a testament to the dynamic nature of manufacturing. Experienced professionals understand that maintaining a competitive edge requires a commitment to continuous improvement, adaptability to new technologies, and adherence to the highest standards of quality and safety. Clients rely on the expertise and reputability of these manufacturers to deliver products that meet specific needs, exemplifying the essence of Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness on which the industry's success hinges.


The expertise required in a pipe mill extends beyond mere operation. It involves understanding market demands, which drive production rates and product diversity. Experience shows that keeping abreast of technological innovations is crucial. For instance, the adoption of 3D modeling and automation in pipe design has radically improved precision and efficiency, reducing material waste and production time. Trust in the pipe mill's capabilities is built over time through consistent product quality and compliance with international standards such as ASTM, API, or ISO. These certifications not only validate the manufacturing process but also assure clients of the product's reliability and performance. Established mills often conduct third-party audits and client visits to further enhance transparency and trustworthiness. Indeed, the evolution of pipe manufacturing technology continues to create new opportunities and challenges. Modern mills are integrating smart technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) to monitor equipment health in real-time, predict downtimes, and optimize production schedules. Such advancements not only enhance the production process but also contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient operation. The pipe mill industry, with its blend of traditional practices and cutting-edge innovations, stands as a testament to the dynamic nature of manufacturing. Experienced professionals understand that maintaining a competitive edge requires a commitment to continuous improvement, adaptability to new technologies, and adherence to the highest standards of quality and safety. Clients rely on the expertise and reputability of these manufacturers to deliver products that meet specific needs, exemplifying the essence of Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness on which the industry's success hinges.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024
Related Products