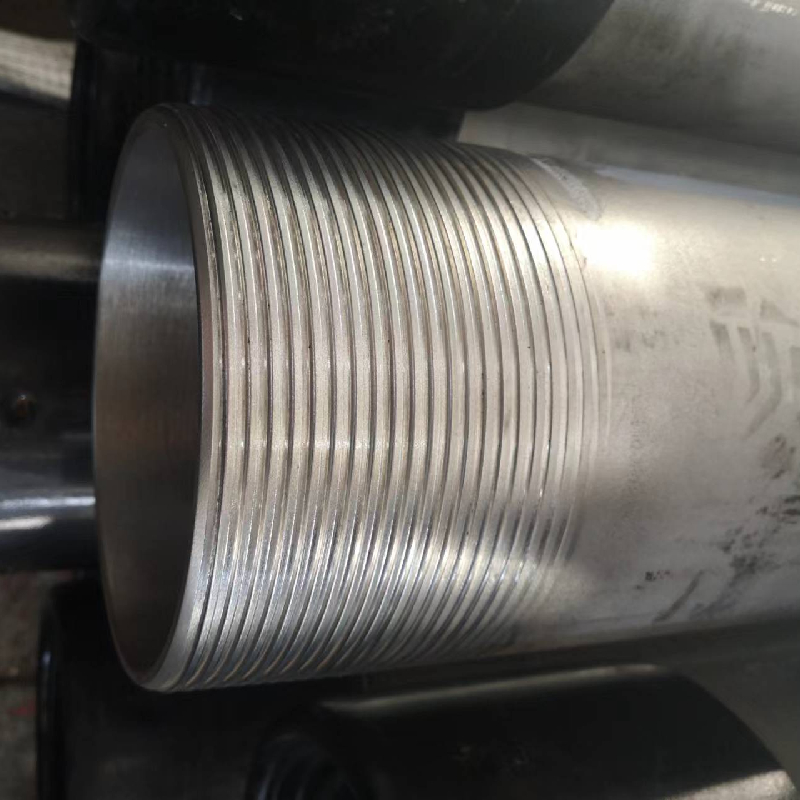
Understanding Steel Pipe Couplings and Their Applications in Various Industries
Understanding Steel Pipe Couplings A Comprehensive Overview
Steel pipe couplings are crucial components used in various industries to connect two sections of pipes seamlessly. They offer a reliable and efficient solution for creating a strong bond, ensuring the safe transportation of fluids and gases. In this article, we will explore the different types of steel pipe couplings, their applications, benefits, and factors to consider when selecting the right coupling for your project.
Types of Steel Pipe Couplings
There are several types of steel pipe couplings, each designed for specific applications
1. Welded Couplings Welded couplings are permanently joined by welding the pipes and the coupling together. This method creates a strong connection but requires skilled labor and proper equipment.
2. Threaded Couplings These couplings feature internal threads that allow the pipes to be screwed together. Threaded couplings are easy to install and can be disassembled, making them ideal for applications where maintenance is necessary.
3. Mechanical Couplings Mechanical couplings use various devices and fittings to connect pipes without welding or threading. They provide flexibility in installation and are often used in applications requiring frequent disassembly.
4. Compression Couplings Compression couplings utilize a tightening mechanism that compresses the pipe ends against the coupling, creating a leak-proof seal. They are commonly used in plumbing and HVAC applications.
Applications of Steel Pipe Couplings
Steel pipe couplings are widely used across several industries, including
- Oil and Gas In oil and gas extraction and transportation, couplings facilitate the joining of pipelines, ensuring efficient flow and minimizing the risk of leaks.
- Construction Steel couplings are extensively used in construction projects for plumbing systems, HVAC installations, and fire suppression systems, providing robust connections between pipes.
- Water Supply Couplings ensure the integrity of water supply systems, facilitating the creation of long pipelines that transport potable water from treatment facilities to consumers.
- Manufacturing Many manufacturing processes require the movement of liquids and gases through piping systems, where couplings play a vital role in maintaining system integrity.
steel pipe coupling

Benefits of Steel Pipe Couplings
Steel pipe couplings offer several advantages
1. Strength and Durability Steel couplings are known for their high tensile strength, making them resistant to corrosion and wear, ensuring a long service life.
2. Versatility Available in various sizes and profiles, steel couplings can accommodate different pipe diameters, making them versatile for numerous applications.
3. Ease of Installation Depending on the type, couplings can be easily installed with the right tools, reducing labor costs and downtime.
4. Maintenance and Repair Many coupling types allow for easy disassembly, facilitating repair and maintenance without the need for complete pipe replacement.
Considerations for Selecting Steel Pipe Couplings
When choosing steel pipe couplings for your project, consider the following factors
- Pipe Material and Size Ensure that the coupling material matches that of the pipes and that it's available in the appropriate size for your application.
- Pressure Ratings Check the pressure ratings to ensure the coupling can withstand the operational pressures of your system.
- Environmental Factors Consider exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures, or moisture, which may require specific types of couplings (such as corrosion-resistant options).
- Installation Method Evaluate whether you’ll need welded, threaded, or mechanical couplings based on your installation capabilities and requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, steel pipe couplings are essential components in various industrial and construction applications. Understanding their types, benefits, and appropriate selection criteria can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of your piping systems. By investing in high-quality steel pipe couplings, you ensure the longevity and reliability of your fluid and gas transportation systems.
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024