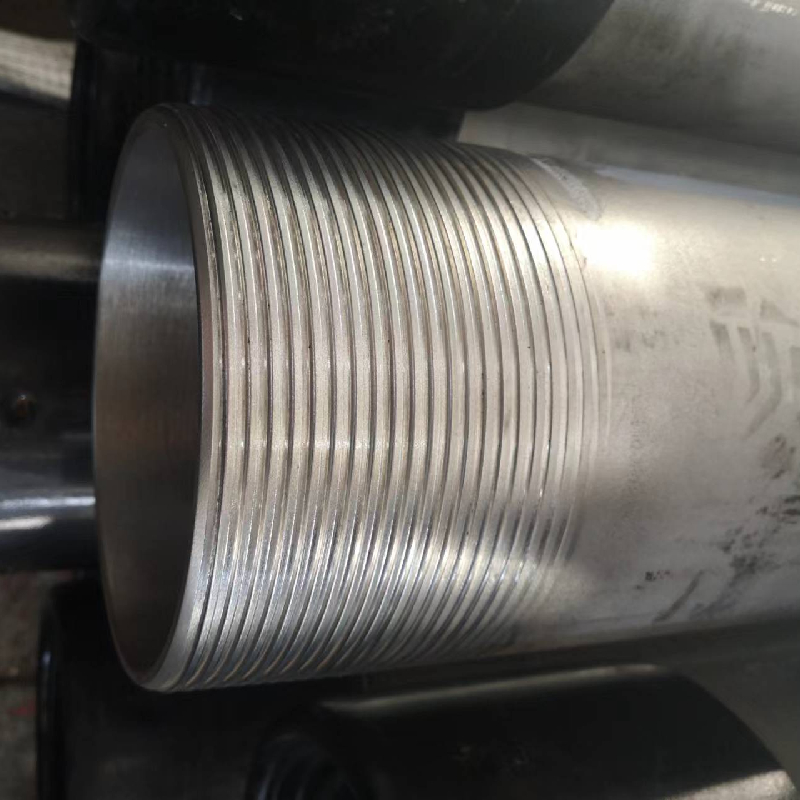
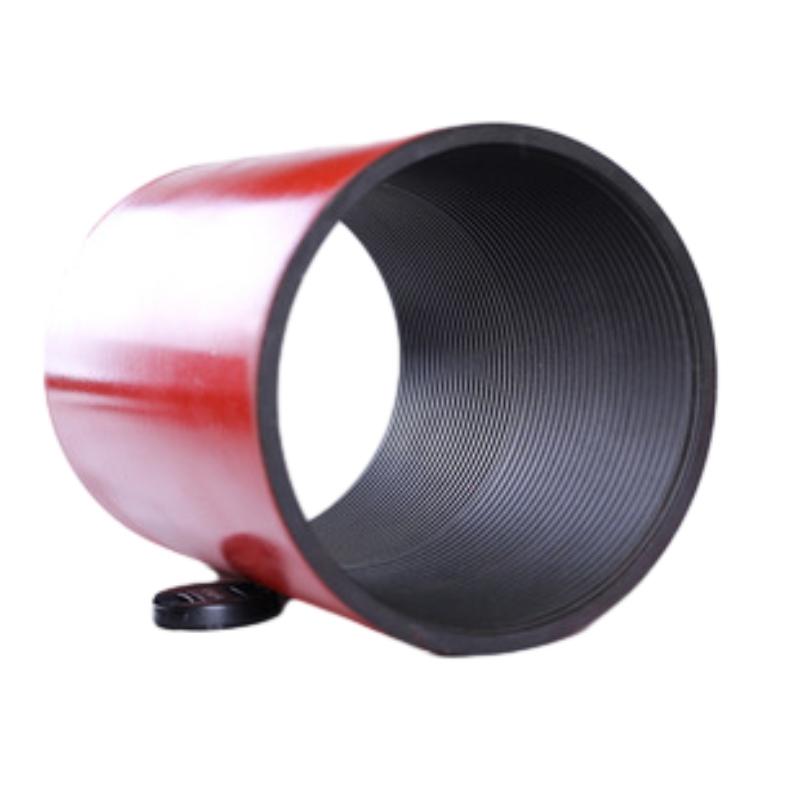
Understanding the Benefits and Applications of Female Threaded Couplings in Plumbing and Engineering
Female Threaded Coupling An Essential Component in Mechanical Engineering
In the field of mechanical engineering, various components are vital for ensuring the functionality and reliability of machines and structures. Among these components, the female threaded coupling is particularly significant. This crucial element plays a pivotal role in connecting pipes, hoses, and other cylindrical objects in various applications. This article explores the characteristics, advantages, applications, and considerations associated with female threaded couplings.
Understanding Female Threaded Coupling
A female threaded coupling is a type of connector characterized by its internal threads that allow it to mate with male-threaded parts. These couplings can be made from a variety of materials, including metals like stainless steel, brass, and aluminum, as well as plastic compositions. The choice of material typically depends on the specific application, considering factors like corrosion resistance, pressure rating, and temperature tolerance.
The internal threads of a female coupling are designed to create a tight seal when mated with a male counterpart, thereby preventing leaks and ensuring a secure connection. In hydraulic and pneumatic systems, where pressure is a critical factor, the integrity of these connections is paramount.
Advantages of Female Threaded Couplings
One of the primary advantages of female threaded couplings is their ease of use. The design allows for straightforward assembly and disassembly without the need for specialized tools. This feature makes them ideal for applications requiring frequent maintenance or inspection.
Their versatility further extends to the variety of sizes and thread standards available. Female couplings can accommodate different diameters and thread types, making them suitable for diverse applications across various industries, including plumbing, manufacturing, and automotive.
Additionally, these couplings provide a robust connection that can withstand significant pressure, making them ideal for high-stress environments. They can effectively handle vibrations and thermal expansions, contributing to the durability and longevity of the overall system.
female threaded coupling

Applications of Female Threaded Couplings
Female threaded couplings find applications across a wide range of industries. In plumbing, they are often used to connect pipes carrying water and other fluids. Their ability to create a leak-proof seal is critical in preventing water damage and maintaining system efficiency.
In the oil and gas industry, these couplings are employed in various pipelines to facilitate the transfer of crude oil, natural gas, and other hydrocarbons. The high-pressure requirements of these systems demand reliable connections that female threaded couplings provide.
Moreover, in the automotive sector, they are utilized in fuel and hydraulic lines, where they ensure safe and efficient fluid transfer. Their resistance to environmental factors, such as corrosion and temperature fluctuations, extends their usability even in harsh conditions.
Considerations for Use
While female threaded couplings offer numerous benefits, certain considerations must be made before their application. Proper selection of size and material is crucial to ensure compatibility with the existing system and to withstand the operating conditions. Additionally, users must comply with industry standards regarding installation and maintenance to avoid potential failures.
Moreover, it is essential to ensure that threads are correctly aligned during assembly. Misalignment can lead to cross-threading, weakening the connection and potentially causing leaks or failures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, female threaded couplings are integral components in many mechanical systems, providing secure connections that are essential for operational efficiency. Their advantages, including ease of use and versatility, along with wide-ranging applications, make them a preferred choice in various industries. However, careful consideration must be given to their selection and installation to maximize their effectiveness and ensure the safety and reliability of the systems in which they are used. As technology advances, the design and materials used for these couplings will continue to evolve, enhancing their performance and expanding their applications even further.
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024