2 月 . 16, 2025 03:51
Back to list
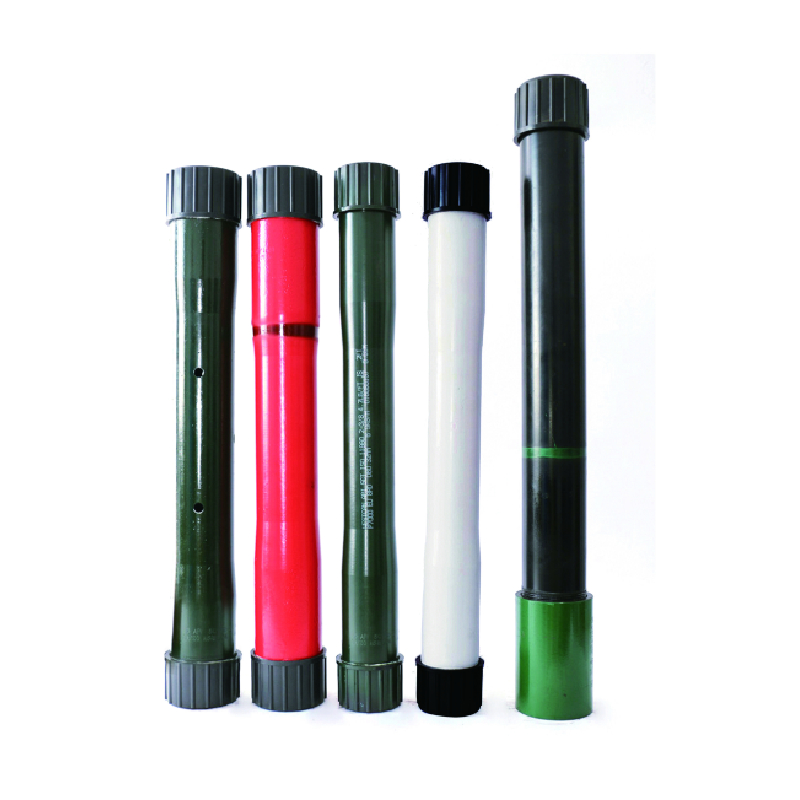
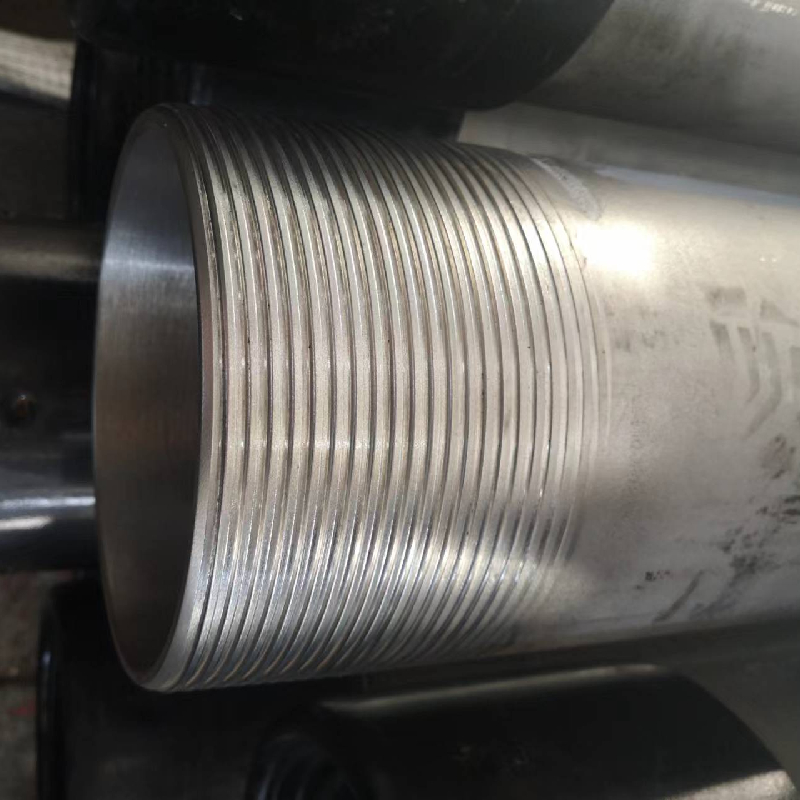
what is a bull plug
The term bull plug might not be widely recognized by those outside of specific technical or industrial fields, yet it plays a significant role in various applications, notably in the oil and gas industry. Its importance stems from its utility in maintaining safety and efficiency within drilling operations. This article delves into the detail surrounding bull plugs, exploring their design characteristics, usage, industry applications, and safety considerations.
Authoritativeness is evident in industry guidelines and standards governing the manufacture and use of bull plugs. Organizations such as the American Petroleum Institute (API) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provide comprehensive specifications that manufacturers and end-users must adhere to. These standards ensure that bull plugs are capable of withstanding the harsh conditions they may encounter, such as high-pressure environments typical of deep-sea drilling operations. Trustworthiness in the industry comes from adhering to established protocols and leveraging products from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and compliance with international safety standards. For companies operating within high-risk industries, partnering with a reputable supplier of bull plugs is not just about ensuring operational efficiency but also about safeguarding their workforce and mitigating environmental risks. Industries outside of oil and gas are beginning to acknowledge the importance of using proper sealing mechanisms like bull plugs. Industries dealing with chemical processing, water treatment, and even construction are deploying similar technologies for pipeline sealing due to the proven reliability of bull plugs. As the broader industrial landscape evolves with an increasing focus on safety and sustainability, the adoption of bull plugs is expected to expand. In conclusion, bull plugs, though seemingly simple, are critical components in industries reliant on complex piping systems. Their ability to effectively seal pipelines and control fluid transport underscores their importance. Understanding their application, material selection, and adherence to industry standards can significantly enhance operational safety and efficiency. As sectors continue to evolve and prioritize environmental sustainability, the demand for high-quality bull plugs is anticipated to grow, reaffirming their essential role in industrial operations.


Authoritativeness is evident in industry guidelines and standards governing the manufacture and use of bull plugs. Organizations such as the American Petroleum Institute (API) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provide comprehensive specifications that manufacturers and end-users must adhere to. These standards ensure that bull plugs are capable of withstanding the harsh conditions they may encounter, such as high-pressure environments typical of deep-sea drilling operations. Trustworthiness in the industry comes from adhering to established protocols and leveraging products from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and compliance with international safety standards. For companies operating within high-risk industries, partnering with a reputable supplier of bull plugs is not just about ensuring operational efficiency but also about safeguarding their workforce and mitigating environmental risks. Industries outside of oil and gas are beginning to acknowledge the importance of using proper sealing mechanisms like bull plugs. Industries dealing with chemical processing, water treatment, and even construction are deploying similar technologies for pipeline sealing due to the proven reliability of bull plugs. As the broader industrial landscape evolves with an increasing focus on safety and sustainability, the adoption of bull plugs is expected to expand. In conclusion, bull plugs, though seemingly simple, are critical components in industries reliant on complex piping systems. Their ability to effectively seal pipelines and control fluid transport underscores their importance. Understanding their application, material selection, and adherence to industry standards can significantly enhance operational safety and efficiency. As sectors continue to evolve and prioritize environmental sustainability, the demand for high-quality bull plugs is anticipated to grow, reaffirming their essential role in industrial operations.
Latest news
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024
Related Products