1 月 . 20, 2025 03:56
Back to list
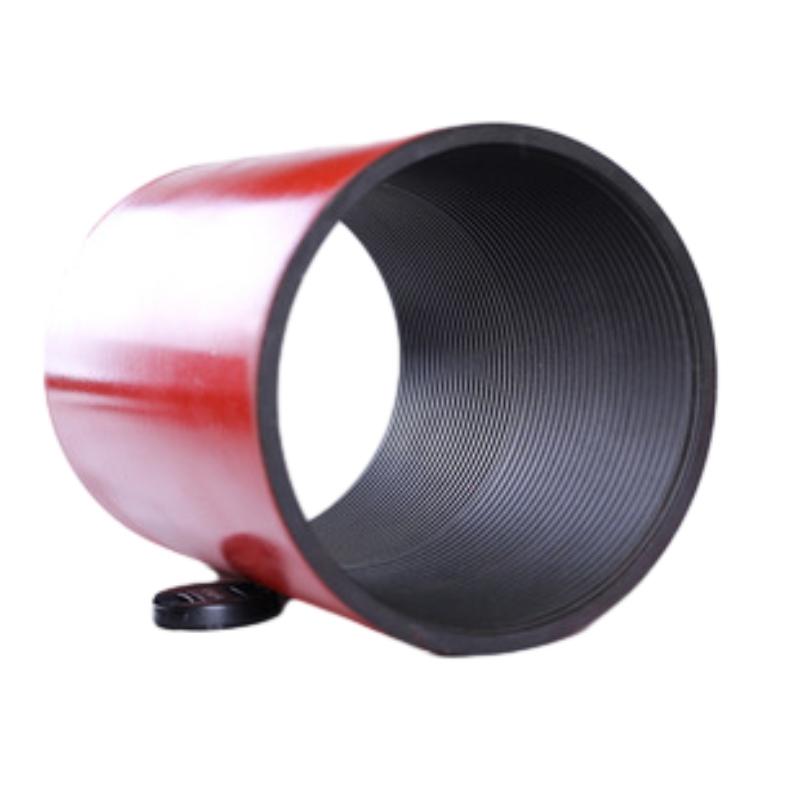
Caing Coupling
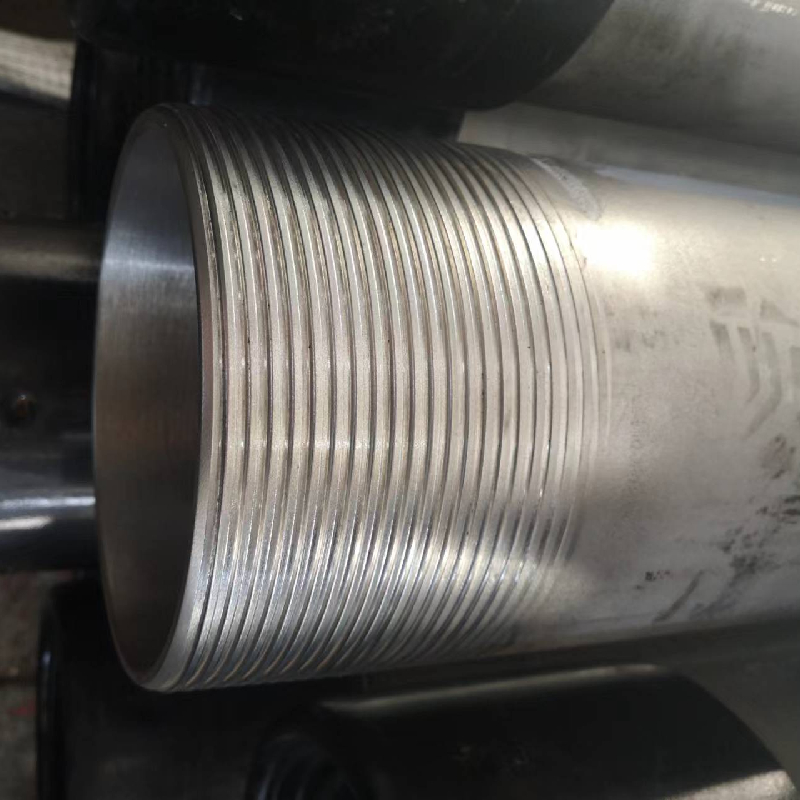
Steel pipe coupling is a crucial component in various applications ranging from residential plumbing to industrial piping systems. The 3-inch steel pipe coupling, in particular, is an essential item that warrants attention for its role in connecting pipes of identical or different sizes and materials. This article delves into the intricate details surrounding 3-inch steel pipe couplings, offering insights that underscore their importance, applications, and merits.
Safety is an unsurpassed priority in any piping operation. 3-inch steel pipe couplings are manufactured following stringent industry standards, ensuring they meet safety requirements for critical applications. These standards often cover various factors, including pressure and temperature ratings, material composition, and dimensional accuracy, which together ensure the coupling's performance under established operational conditions. For plumbers and technicians, ease of installation of 3-inch steel pipe couplings translates to reduced labor time and lowered project costs. The precision in manufacturing ensures snug fits, reducing the need for adjustments or corrections during installation. This not only expedites project completion but also minimizes the potential for leaks, which can be costly and hazardous over time. Despite their inherent advantages, selecting the right 3-inch steel pipe coupling requires a measure of expertise. Factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and the nature of the fluid or gas being transported must guide this choice. Consulting with professionals ensures the right type and specification of coupling is used for the intended application, mitigating future operational risks. In conclusion, a 3-inch steel pipe coupling is an indispensable component in diverse piping systems. Its endurance, flexibility, and safety credentials affirm its standing as a preferred solution for reliable pipe connections. For industries and amateurs alike, understanding these elements fosters informed decision-making, leading to efficient and sustainable solutions for fluid transport challenges.


Safety is an unsurpassed priority in any piping operation. 3-inch steel pipe couplings are manufactured following stringent industry standards, ensuring they meet safety requirements for critical applications. These standards often cover various factors, including pressure and temperature ratings, material composition, and dimensional accuracy, which together ensure the coupling's performance under established operational conditions. For plumbers and technicians, ease of installation of 3-inch steel pipe couplings translates to reduced labor time and lowered project costs. The precision in manufacturing ensures snug fits, reducing the need for adjustments or corrections during installation. This not only expedites project completion but also minimizes the potential for leaks, which can be costly and hazardous over time. Despite their inherent advantages, selecting the right 3-inch steel pipe coupling requires a measure of expertise. Factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and the nature of the fluid or gas being transported must guide this choice. Consulting with professionals ensures the right type and specification of coupling is used for the intended application, mitigating future operational risks. In conclusion, a 3-inch steel pipe coupling is an indispensable component in diverse piping systems. Its endurance, flexibility, and safety credentials affirm its standing as a preferred solution for reliable pipe connections. For industries and amateurs alike, understanding these elements fosters informed decision-making, leading to efficient and sustainable solutions for fluid transport challenges.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlock the Benefits of Pup Joints for Your OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Quality of Casing Couplings from ChinaNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Essential Role of Pup Joints in Drilling OperationsNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Benefits of Tubing Couplings for Your ProjectsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Enhance Your Drilling Operations with Tubing Pup JointsNewsOct.31,2024
-
Elevate Your Drilling Operations with Tubing CrossoversNewsOct.31,2024
Related Products